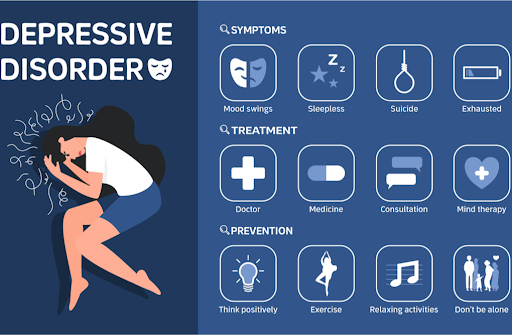
Depression is a
mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is
characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of
interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyed. Depression can
interfere with daily life and make it difficult to perform everyday tasks. It
can also cause physical symptoms, such as fatigue and changes in appetite and
sleep patterns.
Major Causes of
Depression
Genetics:
Depression can run in families and be influenced by genetic factors. However,
it is important to note that genetics alone do not determine whether a person
will develop depression.
Trauma and
Stressful Life Events: Traumatic experiences, such as abuse, losing a
loved one, or a significant life change, can trigger depression. Chronic stress
and ongoing life stressors can also contribute to the development of
depression.
Brain
Chemistry: imbalances in certain chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin,
norepinephrine, and dopamine, can contribute to depression.
Medical
Conditions: Chronic medical conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and
chronic pain, can increase the risk of depression. Certain medications, such as
beta-blockers and interferon, can also cause depression as a side effect.
Substance
Abuse: Substance abuse and addiction can lead to depression or worsen existing symptoms.
Fighting
Depression
Seek
Professional Help: The first step in treating depression is to seek
professional help. A mental health professional can diagnose depression and
develop a treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
Medication:
Antidepressant medication can be effective in treating depression. It is
important to work with a doctor to find the proper medication and dose for you.
Therapy:
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, can effectively treat depression. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a popular form of therapy
that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Lifestyle
Changes: Making positive changes to your lifestyle, such as getting regular
exercise, eating a healthy diet, and practicing good sleep hygiene, can help
reduce symptoms of depression.
Support:
Surrounding yourself with supportive friends and family, or joining a support
group, can help you feel less isolated and provide a sense of community.
Mindfulness and
Relaxation Techniques: Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as
meditation and deep breathing, can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can
contribute to depression.
Healthy Habits:
Engaging in healthy habits, such as regular exercise, good sleep hygiene, and
avoiding drugs and alcohol, can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of
depression.
In conclusion,
depression is a treatable condition and recovery is possible with the proper
treatment and support. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of
depression, seek help from a mental health professional. Remember, you are not
alone, and there is hope for a better tomorrow.


Comments
Post a Comment