Chemical bonding is the forces that hold atoms or ions together in a molecule or crystal. There are several types of chemical bonds, including covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds.
Covalent bonds
occur when atoms share electrons to fill their outermost electron shell, called
the valence shell. The sharing of electrons and forming a stable,
neutral molecule characterize this type of bond. Examples of covalent bonding
can be found in molecules such as water (H2O) and methane (CH4).
Ionic bonds
occur when one atom transfers electrons to another atom, creating ions. This
type of bond is characterized by the transfer of electrons and the formation of
charged ions, called cations and anions. Examples of ionic bonding can be found
in compounds such as sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium oxide (CaO).
Metallic bonds
occur in metals, where the valence electrons of the atoms are not closely tied
to any one atom, but instead are free to move throughout the solid. This type
of bond is characterized by the presence of a "sea" of valence
electrons that are shared among all the atoms in the solid, giving rise to
characteristic metallic properties such as high thermal and electrical
conductivity.
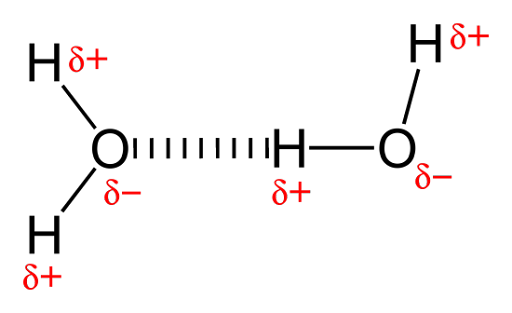
In addition,
there is also a special type of bond called hydrogen bond, which is a type of
dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded
to a highly electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine.
It is important
to note that chemical bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry and plays a
vital role in determining the properties and reactivity of a substance.
Understanding chemical bonding is essential for understanding molecules'
behavior and their interactions.
In conclusion,
chemical bonding is a critical aspect of chemistry that describes the forces
that hold atoms and molecules together. There are several types of chemical
bonds, including covalent, ionic, metallic, and hydrogen, each with unique
characteristics and properties. Understanding chemical bonding is essential for
understanding the behavior of molecules and their interactions.
Read More about
1. Covalent bonding (https://gauravjhaa.blogspot.com/2023/02/covalent-bonding-definition-properties.html)
2. Ionic Bonding (https://gauravjhaa.blogspot.com/2023/02/ionic-bonding.html)
3. Metallic Bonding (https://gauravjhaa.blogspot.com/2023/02/metallic-bonding-definition-properties.html)
4. Hydrogen Bonding (https://gauravjhaa.blogspot.com/2023/01/the-importance-of-hydrogen-bonding-in.html)



Comments
Post a Comment